Animal Cell: Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram

An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall, plant cells have a cell wall.
- Animals are a large group of diverse living organisms that make up three-quarters of all species on earth. With their ability to move, respond to stimuli, respond to environmental changes, and adapt to different modes of feeding defense mechanisms and reproduction, all these mechanisms are enhanced by their constituent elements in the body. However, animals cannot manufacture their own food like plants and hence they depend on plants in one way or another.
- All living things are made up of cells that make up their body structure. Some of these living things are single-celled (unicellular) and other organisms are made up of more than one cell (Multicellular).
- A cell is the smallest (microscopic) structural-functional unit of life of an organism. The cells that constitute an animal are called Animal cells and those that constitute plants are known as plant cells.
- Most cells are covered by a protective membrane known as the cell wall which gives the cells their shape and rigidity.
- Since animal cells lack a rigid cell wall it allows them to develop a great diversity of cell types, tissues, and organs. The nerves and muscles are made up of specialized cells that plant cells cannot evolve to form, hence giving these nerve and muscle cells have the ability to move.
Table of Contents
Interesting Science Videos
Animal cell size and shape
- Animal cells come in all kinds of shapes and sizes, with their size ranging from a few millimeters to micrometers. The largest animal cell is the ostrich egg which has a 5-inch diameter, weighing about 1.2-1.4 kg and the smallest animal cells are neurons of about 100 microns in diameter.
- Animal cells are smaller than the plant cells and they are generally irregular in shape taking various forms of shapes, due to lack of the cell wall. Some cells are round, oval, flattened or rod-shaped, spherical, concave, rectangular. This is due to the lack of a cell wall. Note: most of the cells are microscopic hence they can only be seen under a microscope in order to study their anatomy.
- But animal cells share other cellular organelles with plant cells as both have evolved from eukaryotic cells.
- As noted earlier, animal cells are eukaryotic cells with a membrane-bound nucleus. therefore they have their genetic material in the form of DNA enclosed in the nucleus. They also have several structural organelles within the plasma membrane which perform various specific functions for proper cell function and generally to maintain the body normal mechanisms.
List of 16 animal cell organelles
- Plasma membrane (Cell membrane)
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondria
- Ribosomes
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies/Golgi complex)
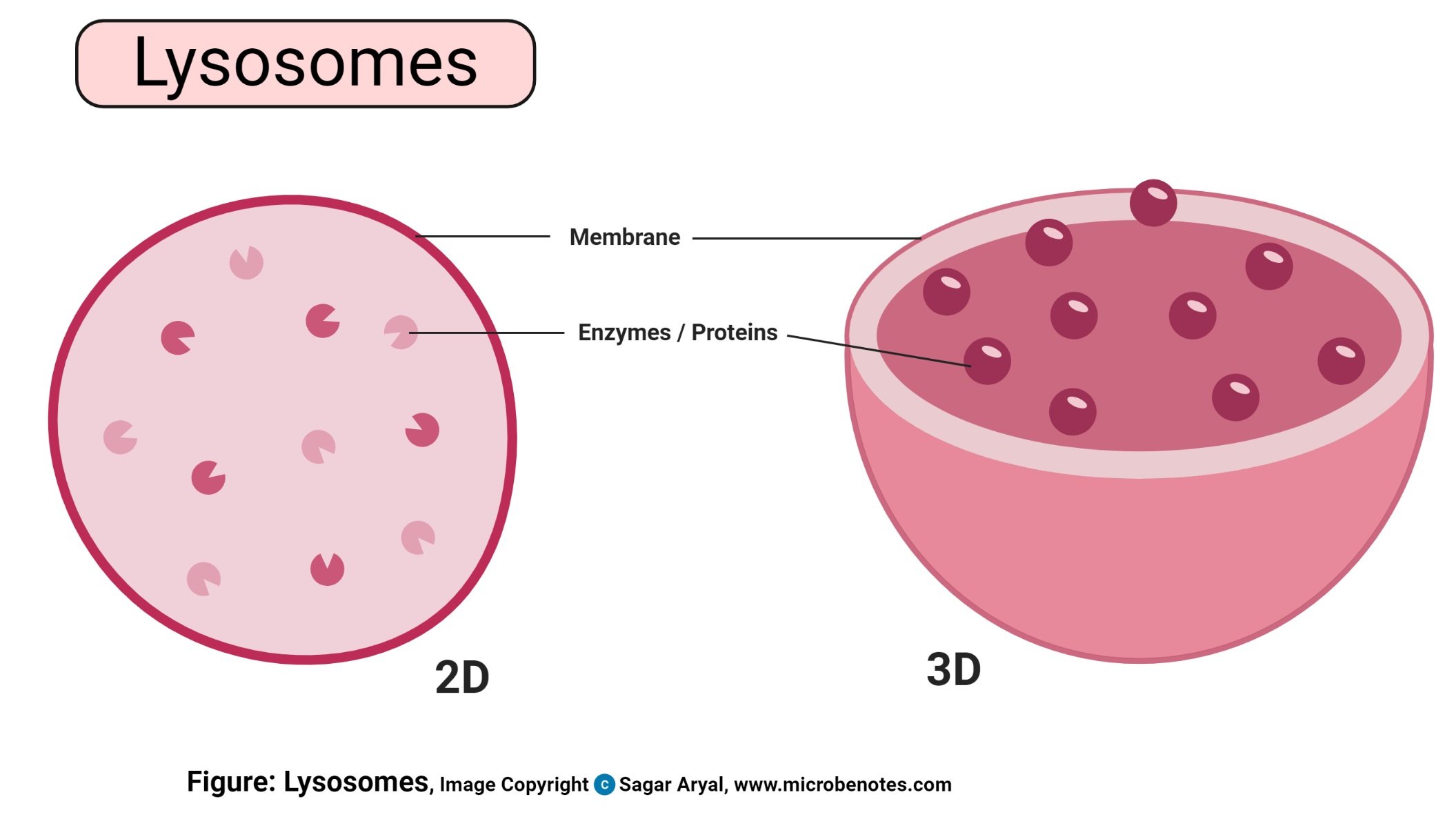
- Lysosomes
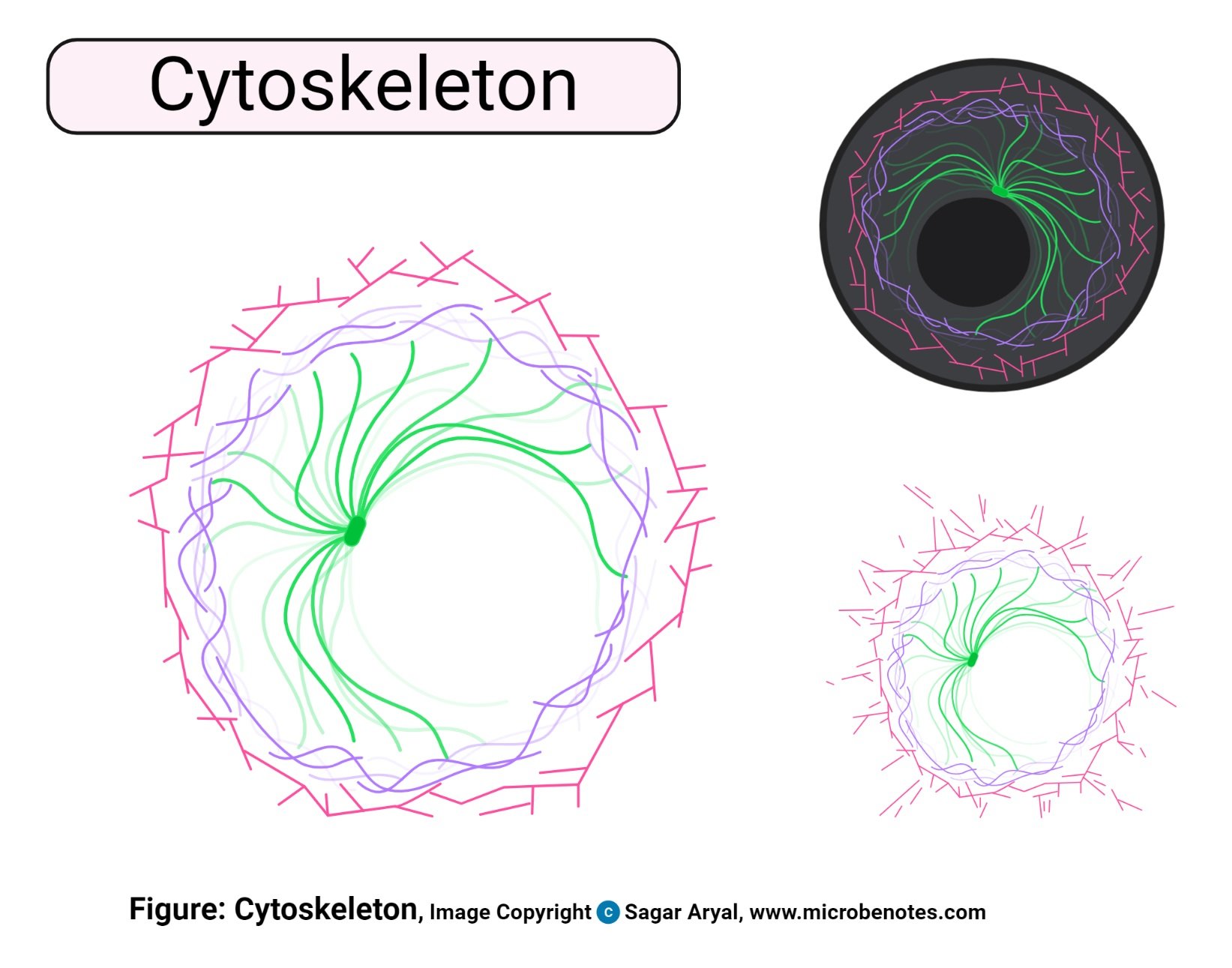
- Cytoskeleton
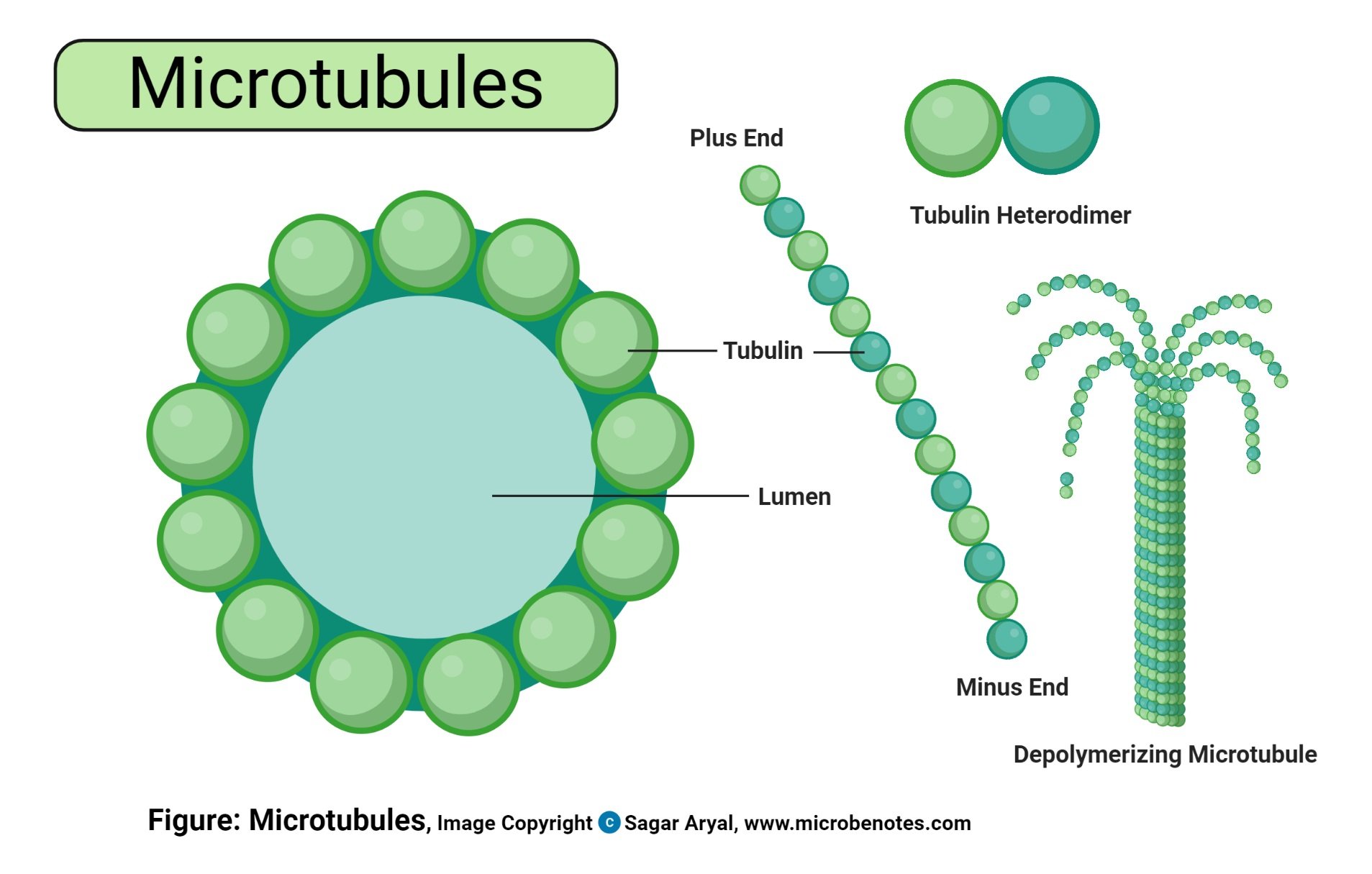
- Microtubules
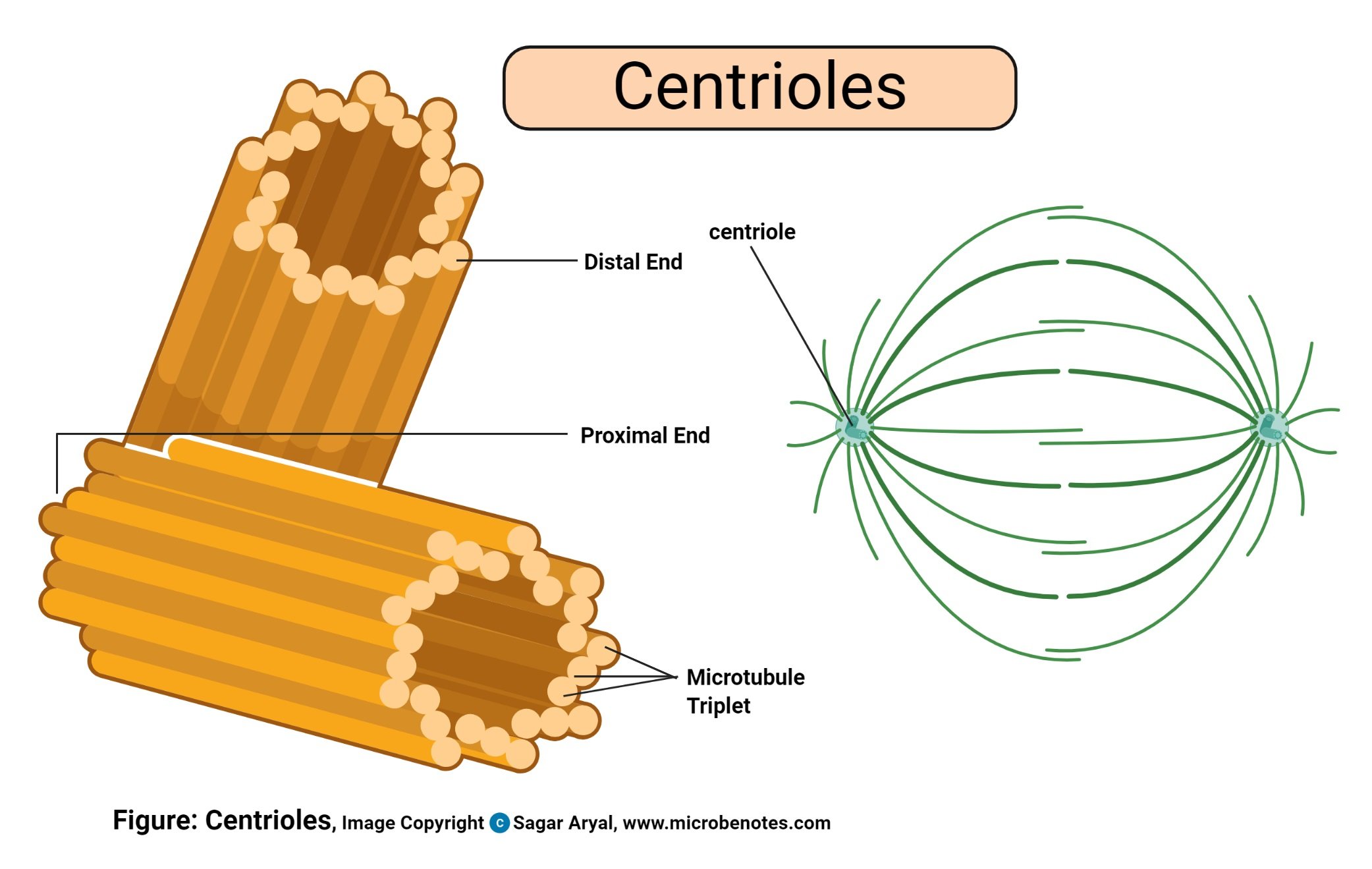
- Centrioles
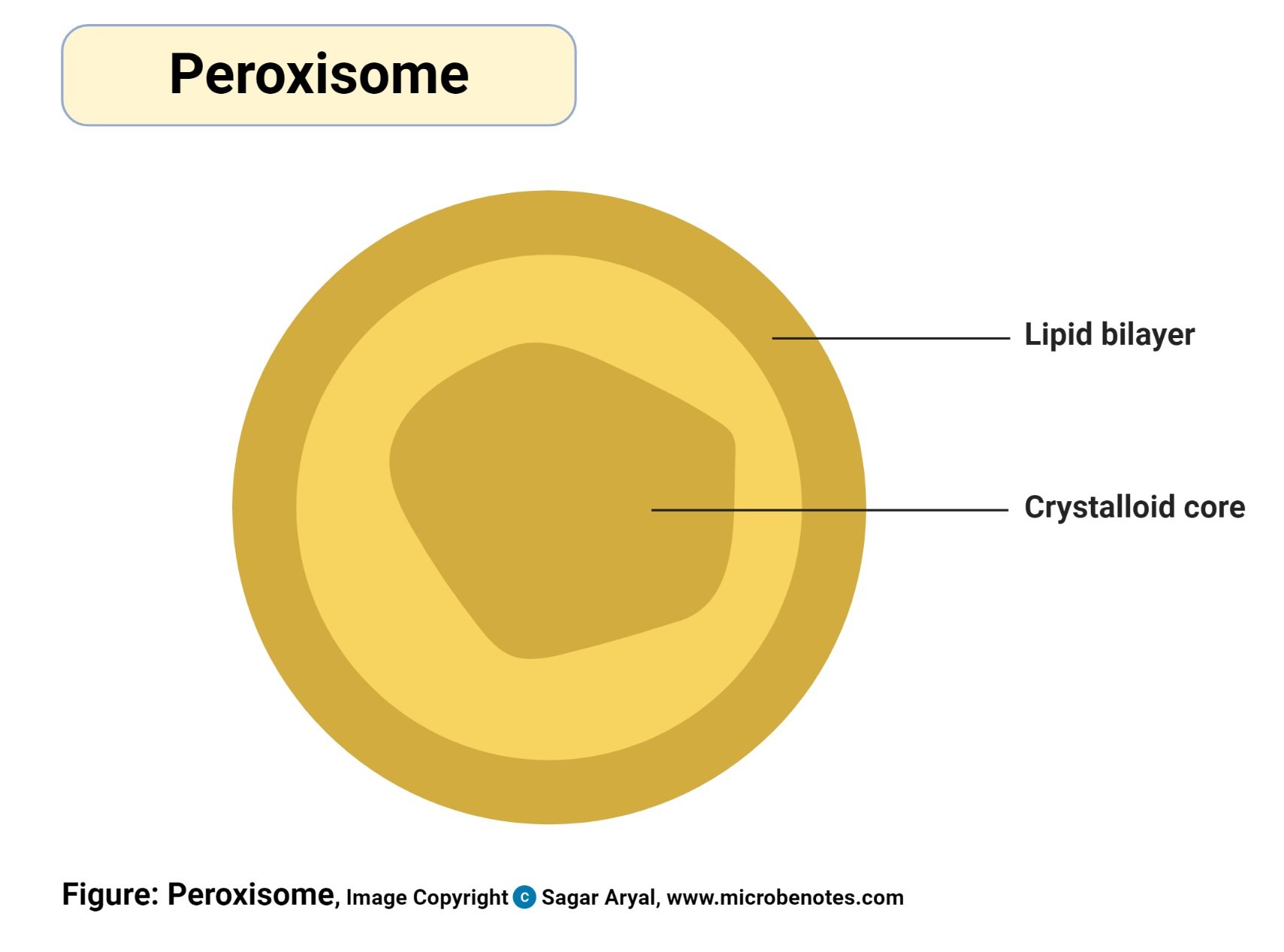
- Peroxisomes
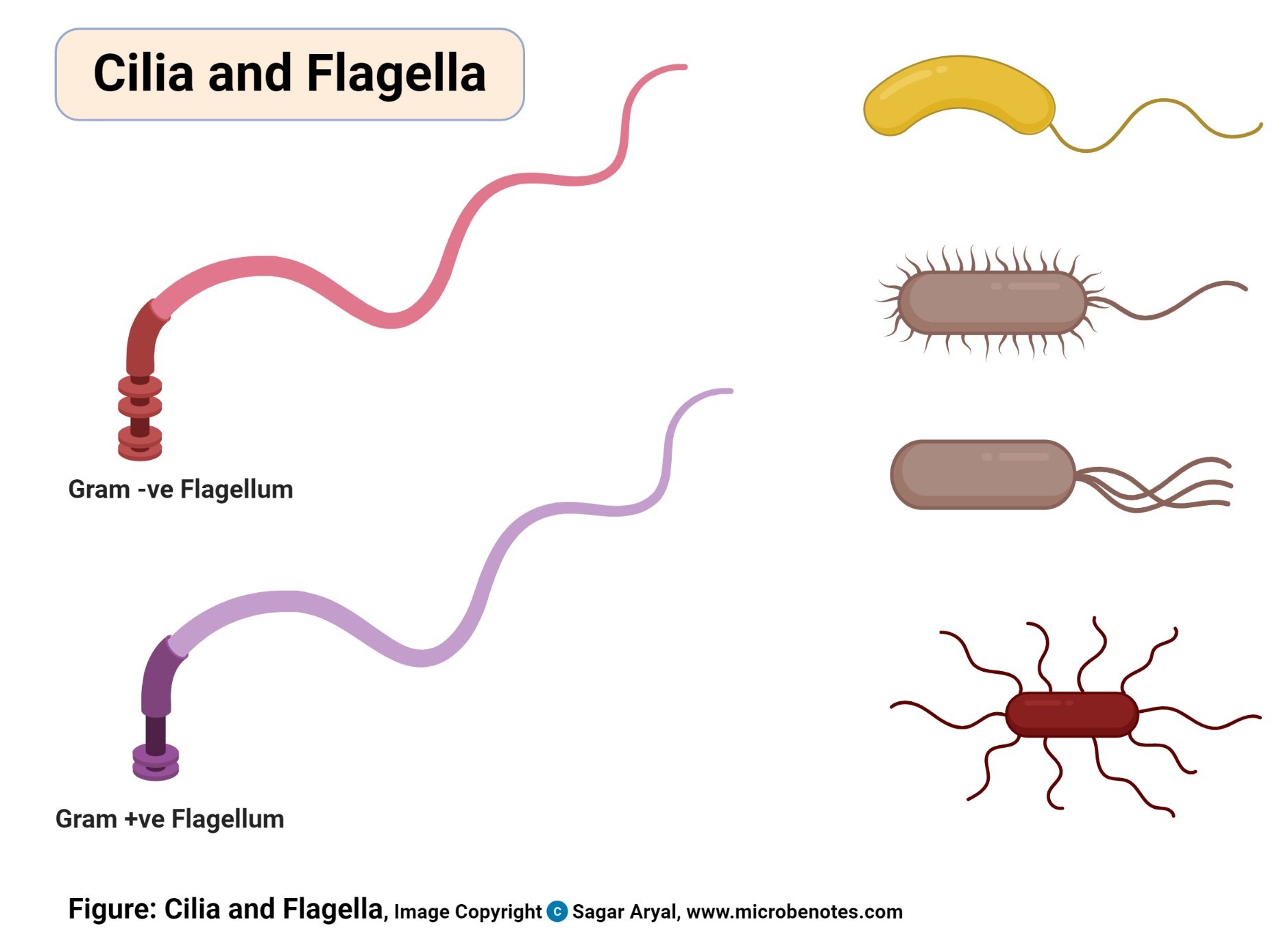
- Cilia and Flagella
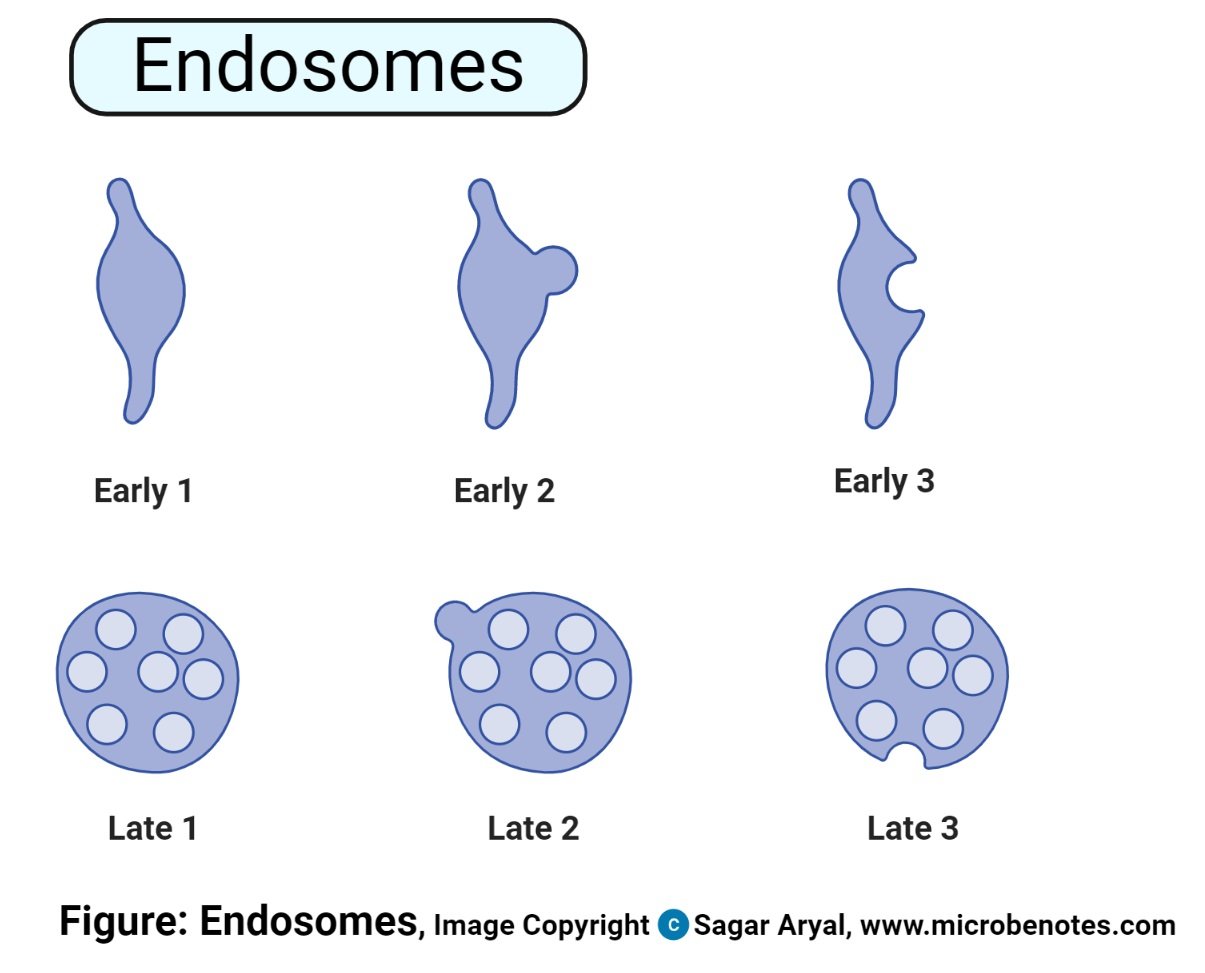
- Endosome
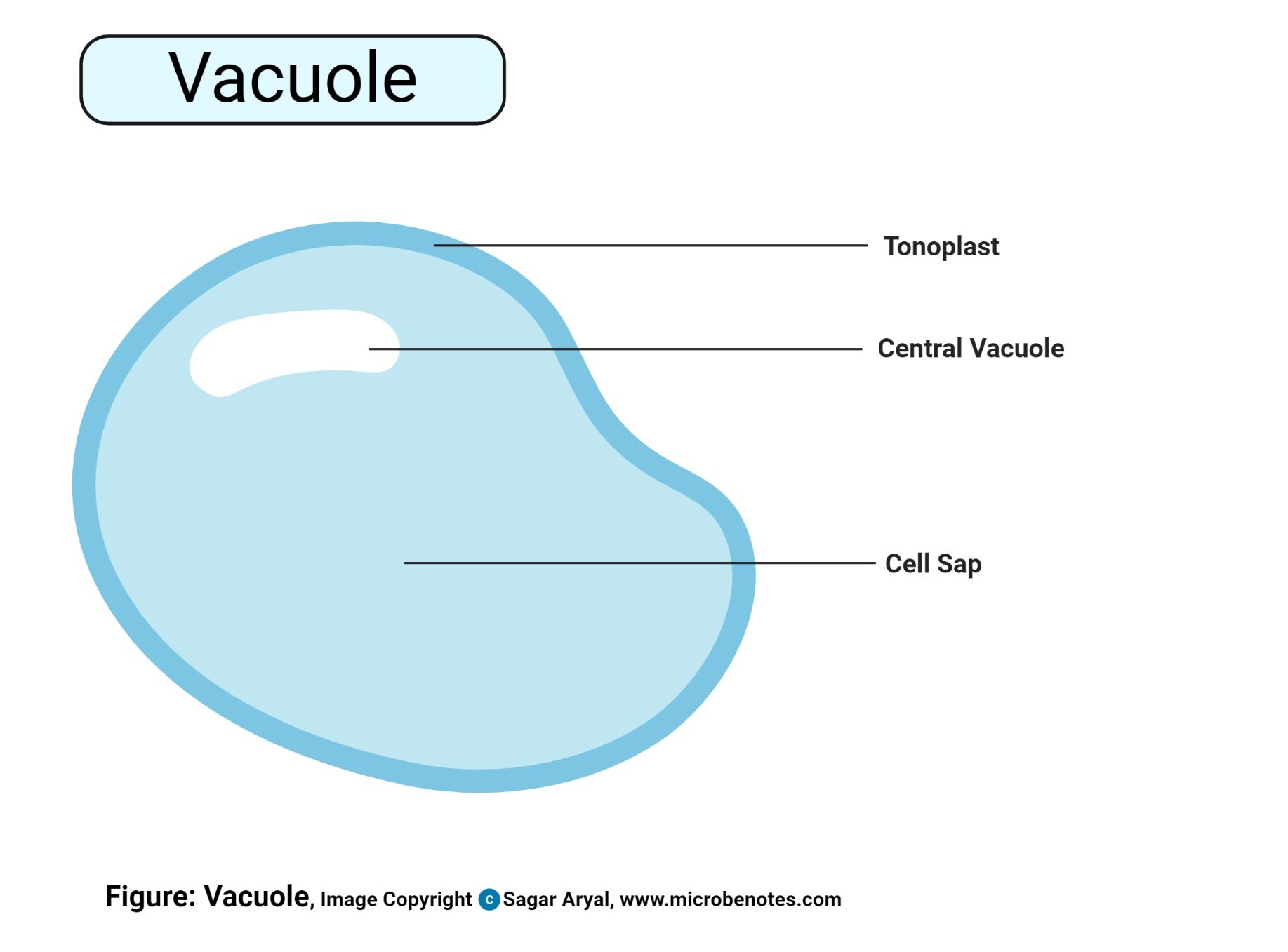
- Vacuoles
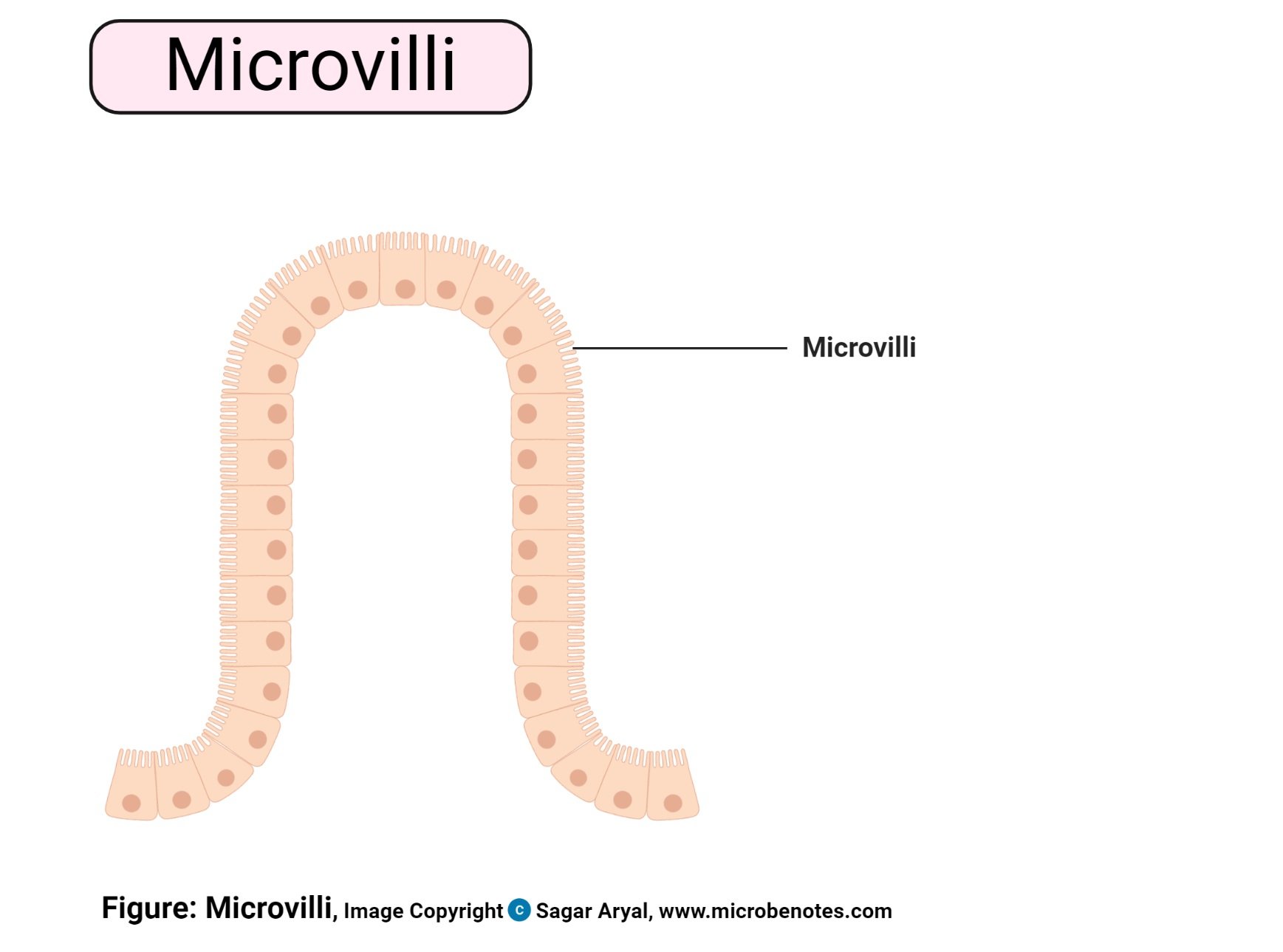
- Microvilli
Animal cell structure
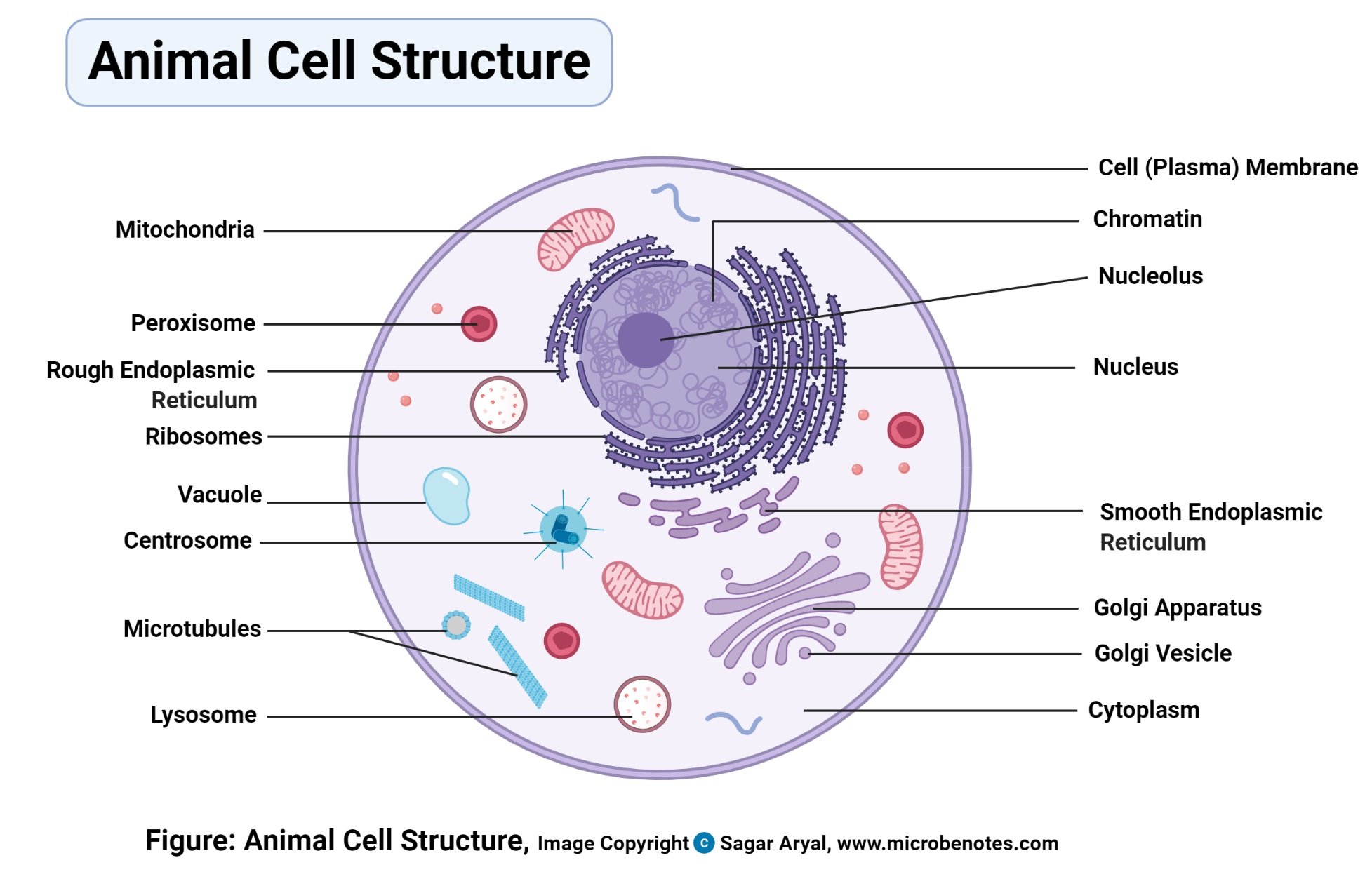
The animal cell is made up of several structural organelles enclosed in the plasma membrane, that enable it to function properly, eliciting mechanisms that benefit the host (animal). The working together of all cells gives an animal its ability to move, to reproduce, to respond to stimuli, to digest and absorb food, etc. Generally, the combined effort by all animal cells is what enables the normal functioning of the body.
Animal Cell Free Worksheet

Animal cell organelles
The major cell organelles include:
Plasma membrane (Cell membrane)
Definition of Plasma membrane (Cell membrane)
It is a thin semipermeable protein-membrane layer that surrounds an animal cell.
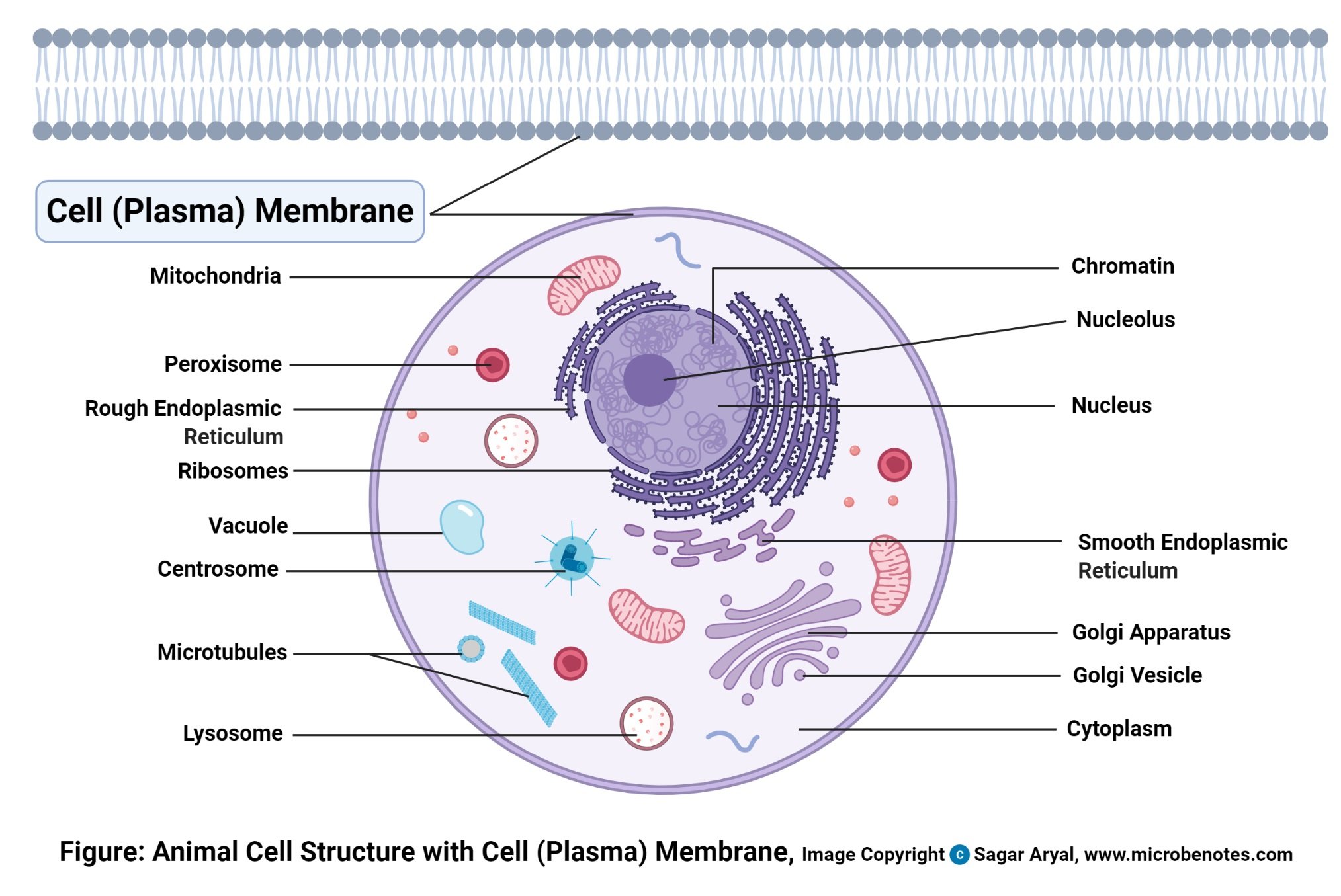
Structure of Plasma membrane (Cell membrane)
- Thin semi-permeable membrane
- It contains a percentage of lipids making a semi-permeable barrier between the cell and its physical environment.
- It has some protein components a
- It is very consistent around the cell
- All living cells have a plasma membrane.
Functions of Plasma membrane (Cell membrane)
- To enclose and protect the cell content
- To also regulate the molecules that pass into and out of the cell, through the plasma membrane. Therefore it controls homeostasis.
- The proteins are actively involved in transporting materials across the membrane
- The proteins and lipids allow cell communication, and carbohydrates (sugars and sugar chains), which decorate both the proteins and lipids and help cells recognize each other.
Nucleus
Definition of Nucleus
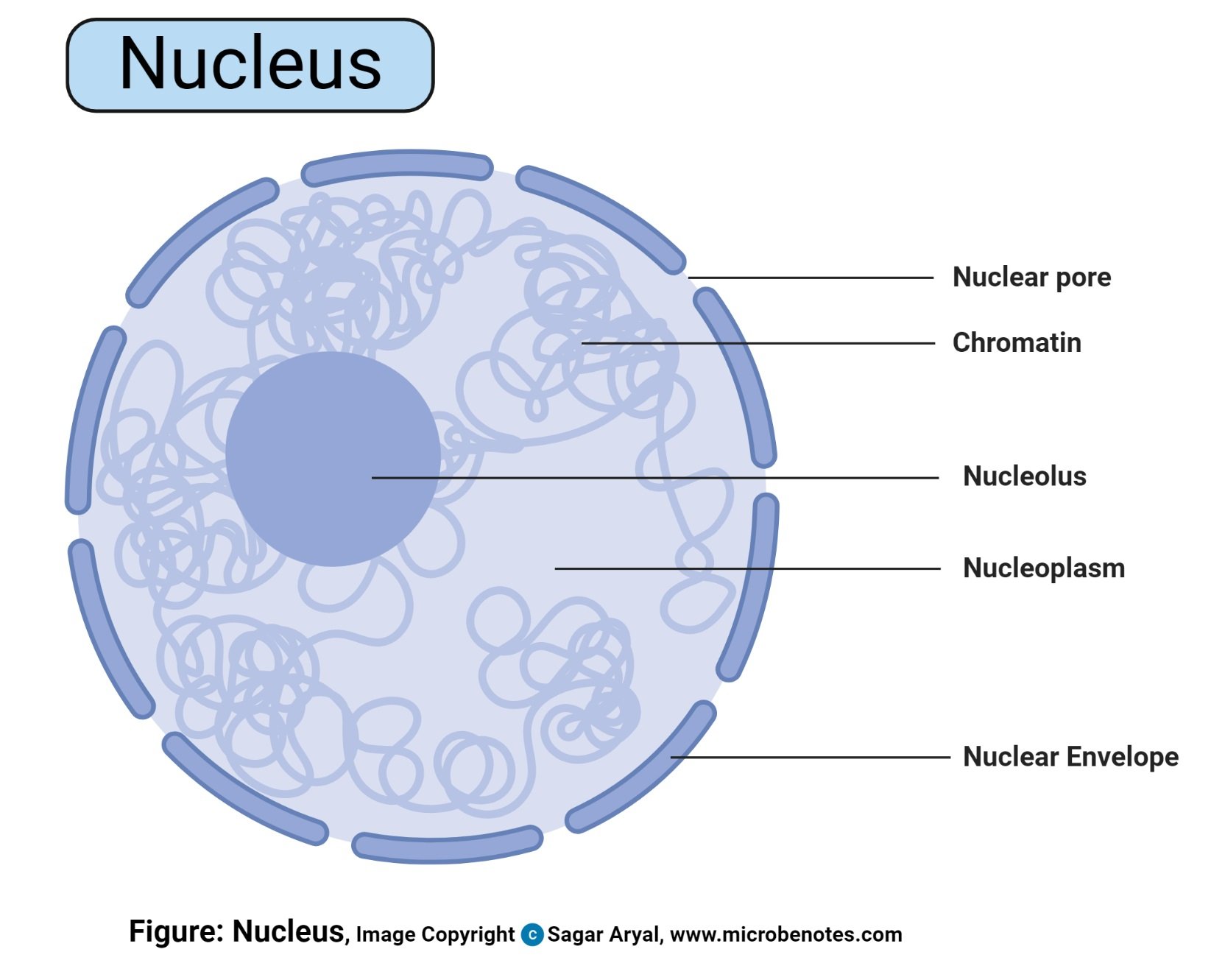
- This is a spherical structured organelle found majorly at the center of a cell surrounded by a double-layered nuclear membrane separating it from the cytoplasm.
- It is held together to the cytoplasm with the help of the filaments and microtubules.
- It holds other cells organelles including the nucleolus, nucleosomes, and chromatins.
- A cell has one nucleus which divides producing multinucleated cells e.g. the skeletal muscle cell fibers.
- Some cells lose their nuclei after maturations e.g. the red blood cells.
Structure of Nucleus
- The double-layered membrane is a continuous channel of membranous from the endoplasmic reticulum network.
- The membrane has pores which allow entry of large molecule
- Nucleoli (Singular; nucleolus) are tiny/small bodies found in the nucleus
- The nucleus and its component organelles are suspended in the nucleoplasm (House of the chromosomal DNA and genetic materials)
Functions of Nucleus
- The primary role of the nucleus is to control and regulate cell activities of growth and maintain cell metabolisms.
- It also carries the genes that have hereditary information of the cell.
- The chromosomal DNA and genetic materials, which are made up of genetic coded ultimately make up their proteins’ amino acid sequences for use by the cell.
- Therefore, the nucleus is the information center.
- It is the site for Transcription (formation of mRNA from DNA) and the mRNA is transported to the nuclear envelope.
Cytoplasm
Definition of Cytoplasm

- This is a gel-like material that contains all the cell organelles, enclosed within the cell membrane.
- These organelles include; Mitochondria, ribosomes, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes intermediate filaments, microfilaments microtubules, vesicles.
Mitochondria
Definition of Mitochondria
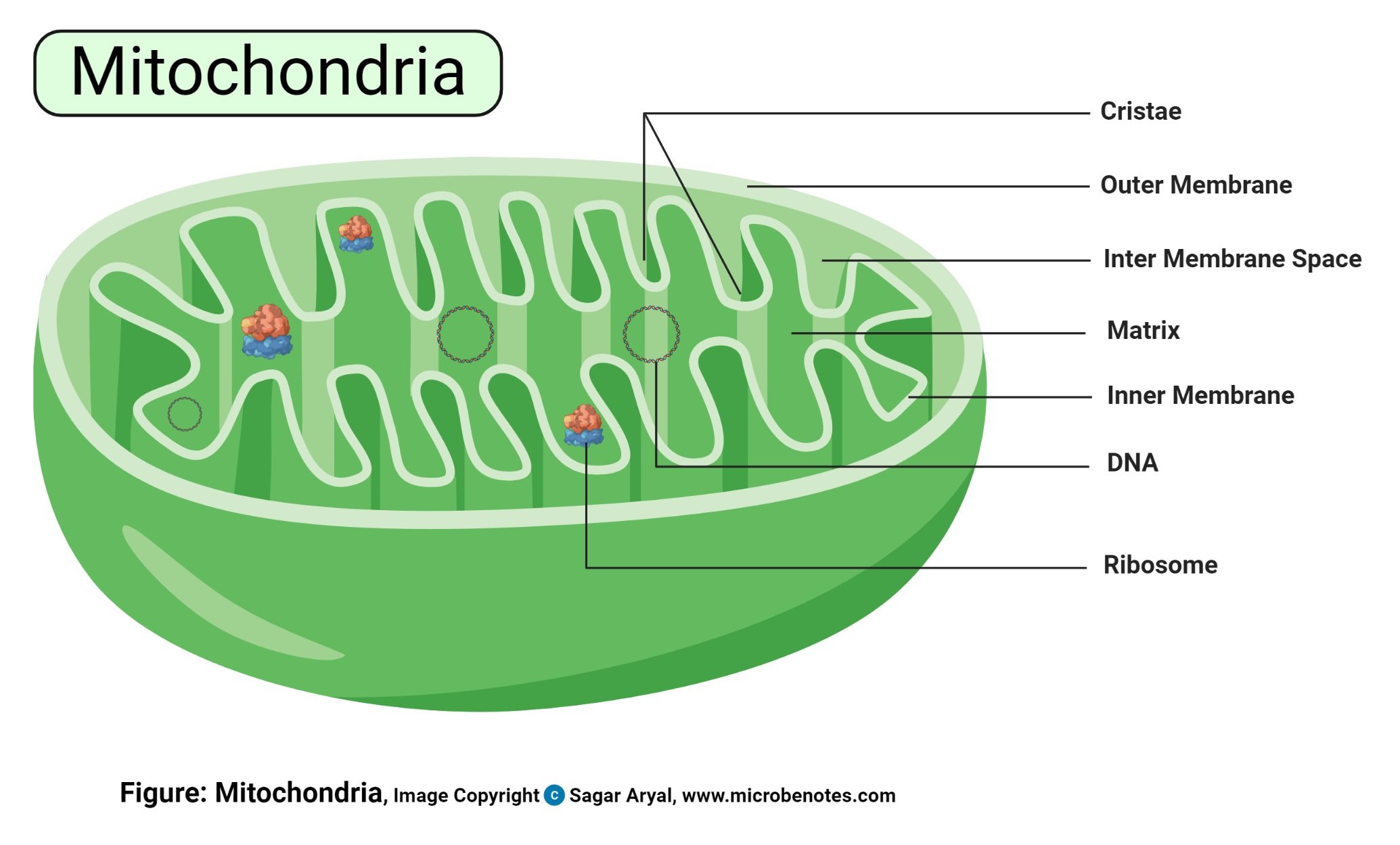
- These are membrane-bound organelles located in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells
- The number of mitochondria found in each cell varies widely depending on the function of the cell it performs.
- For example, erythrocytes do not have mitochondria while the liver and muscle cells have thousands of mitochondria.
Structure of Mitochondria
- They are rod-shaped or oval or spherically shaped, with a size of 0.5 to 10 μm.
- Mitochondria have two special membranes – outer and inner membrane.
- They have a mitochondrial gel-matric in the central mass.
- The membranes bend into folds known as cristae.
Functions of Mitochondria
- Their primary function is to generate energy for the cell i.e they are the power generators, producing energy in form of Adenosine Tri-phosphate (ATP), by converting nutrients and oxygen into energy enabling the cell to perform its function and to also release excess energy from the cell.
- Mitochondria also store calcium which assists in cell signaling activity, generating cellular and mechanical heat and mediating cellular growth and death.
- The outer membrane is permeable, allowing the transport of small molecules and a special channel to transport large molecules.
- The inner mitochondrial membrane is less permeable thus allowing very small molecules into the mitochondrial gel-matrix in the central mass. The gel matrix is composed of the mitochondria DNA and enzymes for the Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle or the Kreb’s Cycle.
- The TCA cycle uses up the nutrients, converting them into by-products that the mitochondria use for producing energy. These processes take place in the inner membrane because the membrane bends into folds called the cristae, where the protein components used for the main energy production system cells, known as the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). ETC is the main source of ATP production in the body.
- The ETC involves several sequences of oxidation-reduction reactions to transport electrons from one protein component to another, thus producing energy that is used for phosphorylation of ADP (Adenosine diphosphate) to ATP. This process is called the chemiosmotic coupling of oxidative phosphorylation. This mechanism gives energy to most cellular activities including muscle movement and they power up the general brain function.
- Some if not all proteins and molecules that make up the mitochondria come from the cell nucleus. The mitochondrial nucleus genome has 37 genes of which 13 of these genes produce most of the components of the ETC. However, mitochondrial DNA is very vulnerable to mutations because they don’t possess a large DNA repair mechanism, a common element found in other nuclear DNAs.
- Moreover, Reactive Oxygen Species ((ROS)) also called free radicals are produced in the mitochondrion, because of the preference for abnormal production of free electrons. These electrons are neutralized by antioxidant proteins in the mitochondrion. However, some of the free radicals can damage mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
- Equally, consumption of alcohol can cause damage to the mtDNA because excess ethanol in the body causes saturation of the detoxifying enzymes leading to the production and leakage of highly reactive electrons into the cytoplasmic membrane and into the mitochondrial matrix, combining with other cellular molecules forming numerous radicals that significantly cause cell damage.
- Most organisms inherit the mtDNA from their mother. This is because the maternal egg donates most of the cytoplasm to the embryo while the mitochondria inherited from the father’s sperm is destroyed. This causes the origin of inherited and acquired mitochondrial diseases due to mutations transmitted into the embryo from the maternal and paternal DNA or maternal mtDNA. Such diseases include Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. When mutated mtDNA accumulates over time has been linked to aging and the development of certain cancers and diseases.
- Naturally, mitochondria play a major role in programmed cell death (apoptosis) and due to mutations in the mtDNA can inhibit cell death-causing the development of cancer.
Ribosomes
Definition of Ribosomes
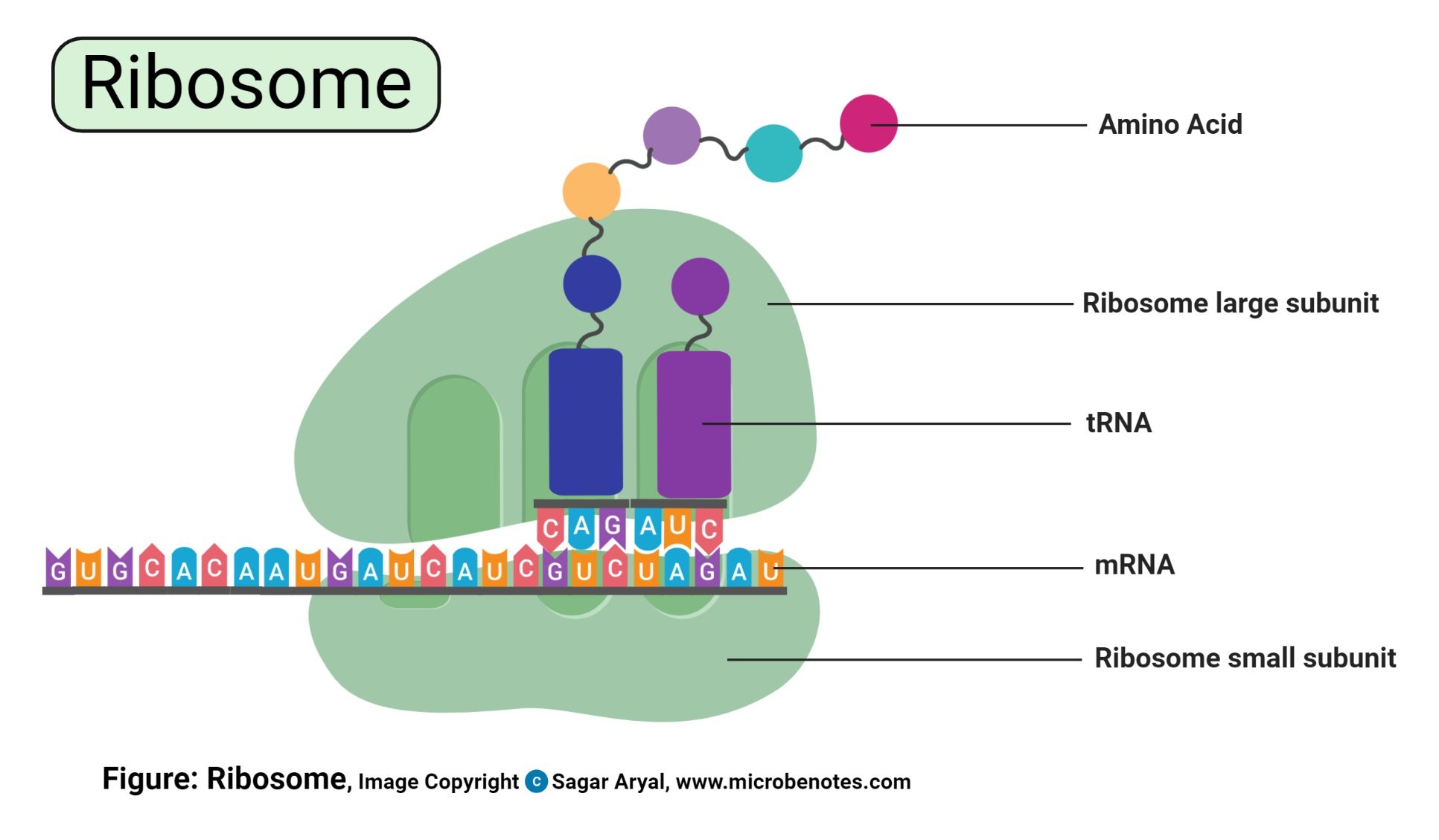
- They are small organelles majorly made up of 60% RNA cytoplasmic- granules and 40% proteins.
- All living cells contain ribosomes, which may be freely circulating in the cytoplasm and some are bound to the endoplasmic reticulum.
- It is the site for protein synthesis.
Structure of Ribosomes
- Ribosomes are made up of ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). In a eukaryotic cell, ribosomes constitute half ribosomal RNA and half ribosomal proteins.
- Each ribosome is made up of two subunits i. e large subunit and small subunit with their own distinct shapes. These subunits are designated as the 40s and 60s in the animal cell.
Functions of Ribosomes
- Ribosomes that occur as free particles are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane occurring in large numbers accounting for about a quarter of the cell organelles. A single replicated cell has about 10 million ribosomes.
- The ribosomal subunits are the site for genetic coding into proteins. On the ribosomes, the mRNA helps determine the coding for Transfer RNA (tRNA) which also determines the protein amino acid sequences. This leads to the formation of the rRNA which are involved in the catalyzation of peptidyl transferase creating the peptide bond found between the amino acid sequences that develop the proteins. The formed proteins then detach from the ribosomes, migrating to other cell parts for utilization by the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
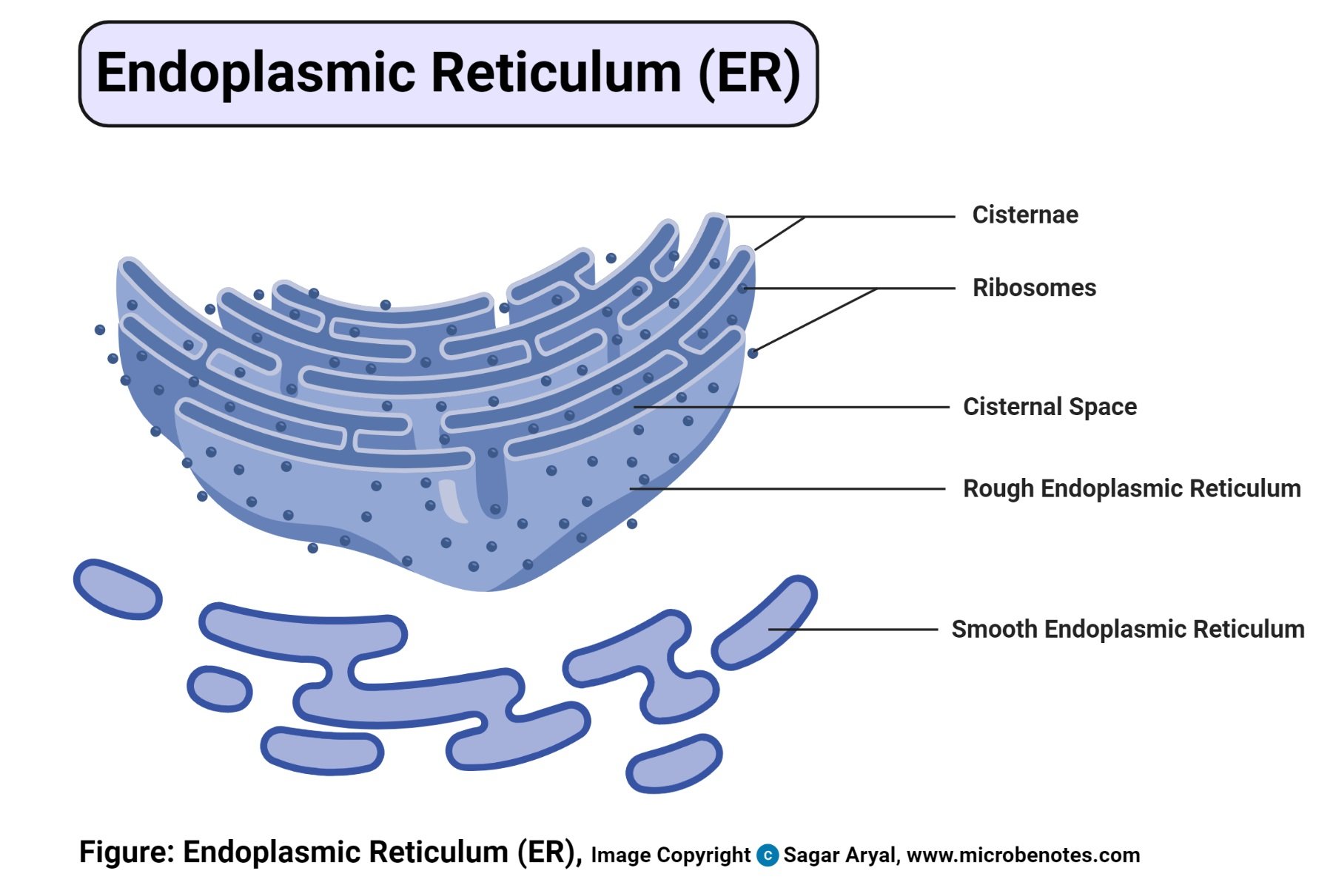
- This is a continuous folded membranous organelle found in the cytoplasm made up of a thin network of flattened interconnected compartments (sacs) that connects from the cytoplasm to the cell nucleus.
- Within its membranes, there are membranous spaces called the cristae spaces and the membrane folding are called cristae.
- There are two types of ER based on their structure and the function they perform including Rough Endoplasmic reticulum and the Smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
Functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Manufacturing, processing and transporting proteins for cell utilization both in and out of the cell. This is because it is directly connected to the nuclear membrane providing a passage between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
- The ER has more than half the membranous cell content, hence it has a large surface area where chemical reactions take place. They also contain the enzymes for almost all the cell lipid synthesis hence they are the site for lipid synthesis.
The variation in physical and functional characteristics differentiate the ER into two types i.e Rough endoplasmic reticulum and Smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
Types of Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER) – Rough ER is called “rough” because there surface is covered with ribosomes, giving it a rough appearance. The function of the ribosomes on rough ER is to synthesis proteins and they have a signaling sequence, directing them to the endoplasmic reticulum for processing. Rough ER transports the proteins and lipids through the cell into the cristae. They are then sent into the Golgi bodies or inserted into the cell membrane.
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER) – Smooth ER is not associated with ribosomes and their unction is different from that of the rough endoplasmic reticulum, despite lying adjacent to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Its function is to synthesis lipids (cholesterol and phospholipids) that are utilized for producing new cellular membranes. They are also involved in the synthesis of steroid hormones from cholesterol for certain cell types. It also contributes to the detoxification of the liver after the intake of drugs and toxic chemicals.
- There is also a specialized type of smooth ER known as the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Its function is to regulate the concentration of Calcium ions in the muscle cell cytoplasm.
Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies/Golgi complex)
Structure of Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies)
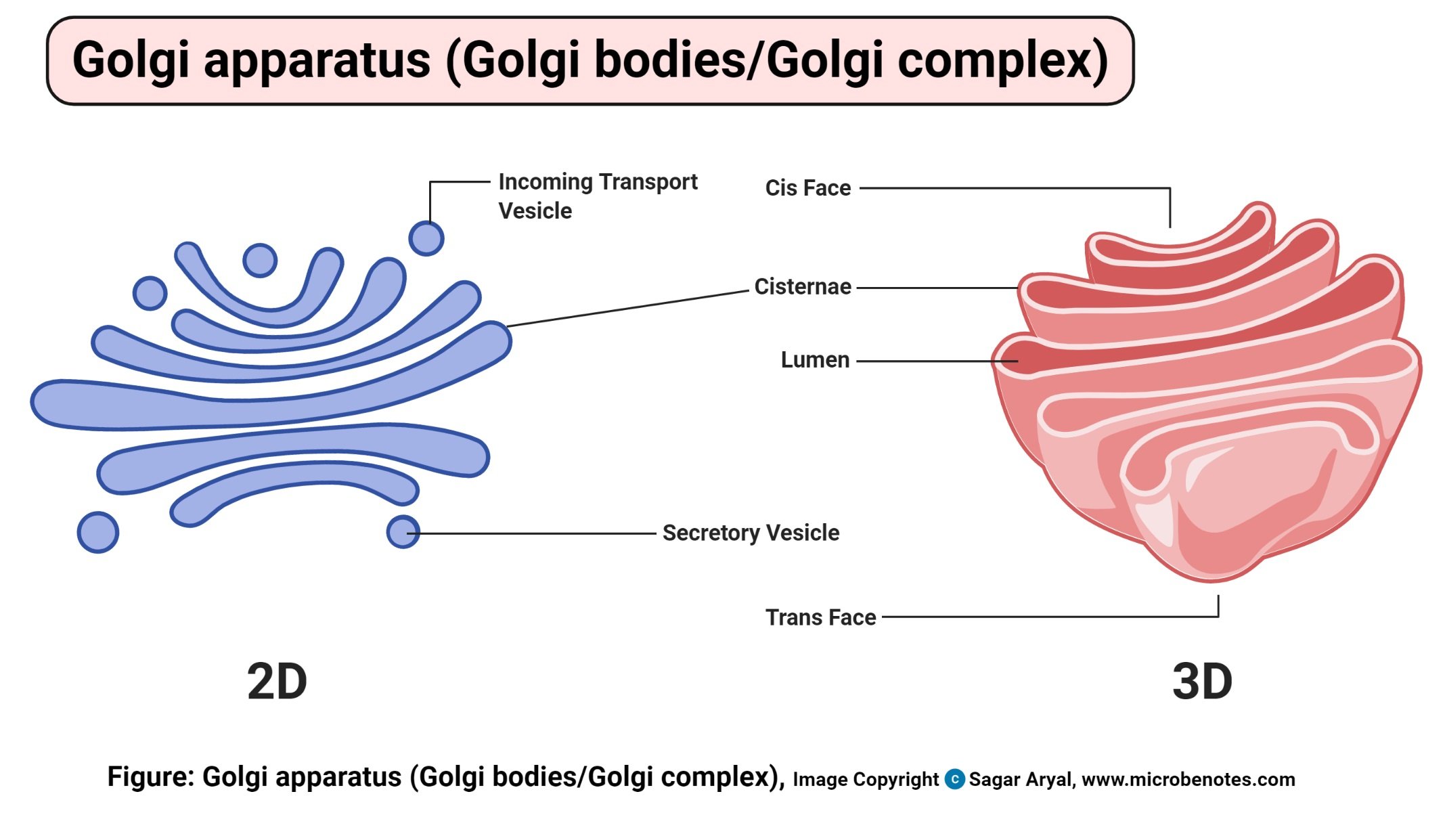
- These are membrane-bound cell organelles found in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell, next to the endoplasmic reticulum and near the nucleus.
- Golgi bodies are supported together by cytoplasmic microtubules and held by a protein matrix
- It is made up of flattened stacked pouches known as cisternae.
- These cisternae may be 4- 10 in number for animal cell Golgi bodies though some organisms like single-celled organisms have about 60 cisternae.
- They have three primary compartments known as cis (Cisternae Nearest the Endoplasmic Reticulum), medial (central layers of cisternae) and the trans (cisternae farthest from the endoplasmic reticulum).
- Animal cells have very few (1-2) Golgi bodies while plants have a few hundred.
Functions of Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies)